Assets mean the value, a thing or property owned from where you can get economic benefit in the future or present. Simply, you can say that which helps you in generating future income or cash flow in a company, small business, proprietorship or an organization. The only thing which is useful in generating income is called the Assets.
- TYPES OF ASSETS | Classification of Assets
- ACCORDING TO THEIR CONVERTIBILITY ASSETS ARE OF TWO TYPES:
- ACCORDING TO THEIR PHYSICAL NATURE ASSETS ARE OF TWO TYPES:
- ON THE BASIS OF THEIR USAGE FOR BUSINESS OPERATION ASSETS ARE DIVIDED INTO TWO PARTS:
- ASSETS ARE EQUALS TO (Formula):
- FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING ASSETS:
- ECONOMIC ASSETS:
- BUSINESS ASSETS:
- DEPRECIATION OF ASSETS
- FACTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR CAUSING DEPRECIATION
- SYNONYMS OF ASSETS
- ASSET CLASSES
- EQUITIES – Also called stocks.
- FIXED INCOME – Also called bonds.
- CASH EQUIVALENTS
- ASSET MANAGEMENT
- Asset management is important:
- ASSET TURNOVER RATIO
- ASSET VERIFICATION
- ASSET FREEZE
- ASSET TRACKING
- ASSETS: DEBIT OR CREDIT
- HOW ASSETS AFFECT THE BUSINESS?
- ASSET VS LIABILITY
- HOW ASSETS TURN INTO LIABILITIES?
- Liabilities are meant for:-
- HOW LIABILITIES CAN TURN INTO ASSETS?
These are the valuable things purchased by a company from which company gets benefits in the future in generating income. Assets are brought in business to increase the level of the business as they are capable of generating cash flow in the business. Assets may be tangible or intangible which has a monetary value and will be helpful in generating future cost benefits.

EXAMPLES of assets:-
- Building
- Land
- Car
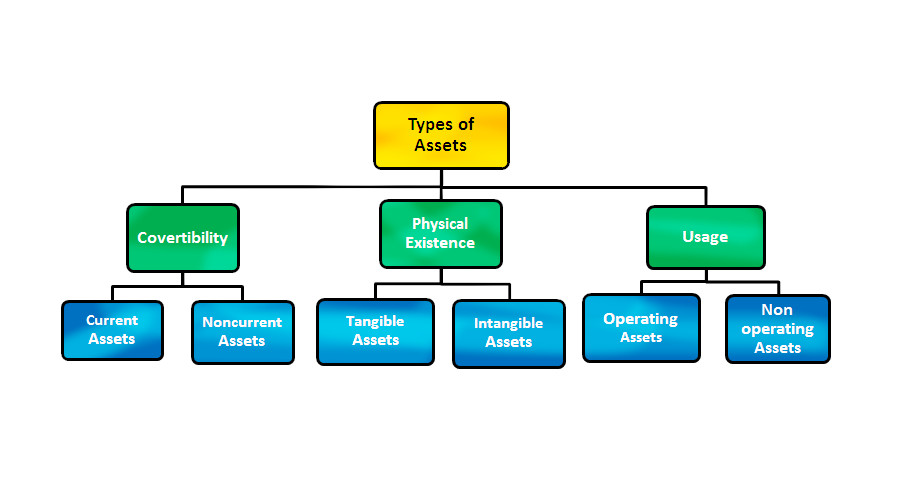
TYPES OF ASSETS | Classification of Assets
Assets are categorized/classified in different categories according to their convertibility, physical nature and their usage.
ACCORDING TO THEIR CONVERTIBILITY ASSETS ARE OF TWO TYPES:
- Current assets
- Non-current assets
Current assets are those assets which can be easily convertible into cash. They are short-term assets as they take a short time to convert into cash as compared to the fixed assets. Current assets are also known as liquid assets.
EXAMPLE- fixed deposit, bank balance, short-term investments, etc.
Non- current or Fixed assets are those assets which are of fixed nature. It means that they could not be easily convertible into cash. To convert this into cash first it includes a long procedure, then takes time for their sale, after that it will be converted into cash. Non-current assets are also known by many other names such as fixed assets, long-term assets or hard assets.
EXAMPLE- land, building, furniture, machinery, etc.
ACCORDING TO THEIR PHYSICAL NATURE ASSETS ARE OF TWO TYPES:
- Tangible assets
- Intangible assets
Tangible assets are those assets which we can feel, see, touch. All fixed assets are categorized as tangible assets because their physical existence. Some current assets which has physical existence are also included in tangible assets such as cash, etc.
Intangible assets are those which we can not see, feel or touch but they have value to give benefit in the future such as patent, etc.
- Operating assets
- Non-operating assets
ON THE BASIS OF THEIR USAGE FOR BUSINESS OPERATION ASSETS ARE DIVIDED INTO TWO PARTS:
Operating assets are those assets which are used for daily day to day transactions. These are used in business for producing products & services.
Non-operating assets are those assets which are not required for daily business operations.
ASSETS ARE EQUALS TO (Formula):
TOTAL ASSETS formula= TOTAL LIABILITIES + TOTAL CAPITALS
NET ASSETS calculation= TOTAL ASSETS – TOTAL LIABILITIES
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING ASSETS:
In financial accounting, an asset could be any thing which is owned by the business. It can be tangible or non-tangible that can be controlled to produce future economic value. The balance sheet records the monetary value of the asset owned by the business.
ECONOMIC ASSETS:
Economic assets are those assets which are recorded in the balance sheet of the system. So, these assets are defined as the authority
- over which ownership rights are applied by an institutional unit, individually.
- from which economic benefits can be derived by the owner by using them for a period of time or by holding them.
BUSINESS ASSETS:
Business assets are those assets that a business owns to get economic benefits from them. Examples of business assets are cash, building, equipment, office furniture, etc.
DEPRECIATION OF ASSETS
With time the value of some (usually fixed asset) asset decreases. This decreases in value will be categorized as an expense. This fall in value of assets is called depreciation. Depreciation assets are assets which are held by a company which can be used in the production of goods and services, for rental to other, for other business purposes, etc.
FACTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR CAUSING DEPRECIATION
- limited useful life; and
- expiration of time; and
- market changes; and
- usage over a period of time, etc.
SYNONYMS OF ASSETS
- A useful thing or valuable quality: plus, quality, specialty, strong point, strength, resource, advantage, benefiT, boon, bonus, treasure, etc.
- The total of one’s money and property: property, capital, wealth, worth, fortune, riches, savings, etc.
- An item of great value: valuable, collectible, antique, precious item, possession, merchandise, priced possession, etc.
ASSET CLASSES
An asset class is a group of investments which have similar characteristics and behave similarly in the market place. There are mainly three types of asset classes: equities (stocks), fixed income (bonds), cash equivalent or money market instruments.
EQUITIES – Also called stocks.
- Represents the value of the shares issued by an enterprise.
- They show high liquidity.
- Gives above-inflation returns.
- Returns are volatile.
- Equities can be used to achieve long-term goals.
- Example: direct stocks, equity ULIPs, etc.
FIXED INCOME – Also called bonds.
- It is a financial or debt instrument that pays a fixed amount of interest to the investors.
- They show high liquidity.
- Offers near to inflation returns.
- Returns are less volatile.
- Issued by government, cooperation and other entities.
- Bonds can be used to achieve short-term goals.
- Example: debt funds, post office schemes, endowment policies, bonds (govt. cooperate), etc.
CASH EQUIVALENTS
- Investment securities that can be easily convertible into cash.
- They also show high liquidity.
- Below inflation rates.
- No volatile.
- They can be used to store your emergency funds.
- Example: liquid funds, FDs, savings account balance, cash.
ASSET MANAGEMENT
Asset management is a systematic process which involves the management of people’s asset. Thie process includes tangible and intangible assets. This process is used to:
- have control over them.
- lead them.
- make plannings about them.
- organise them in a proper manner.
Asset management is important:
- to manage the assets effectively.
- to improve the productivity and efficiency of a business.
- to utilise the assets in a good manner.
- to utilise them in such a way from where you can get benefit from them.
The purpose of assets management is to keep the track of the assets of the company in a proper manner that can save money and time of the company. Asset management is a process used to maximise the assets of the company and to place a business in a better position. This process also gives us information about assets that:
- where they are located.
- how they are used.
- when and what changes were made to them.
ASSET TURNOVER RATIO
Asset turnover is a financial ratio which measures a company’s ability to generate sales revenue from its assets. In simple words, you can say, it is an efficiency of a business which use their assets to generate sales. So, a higher ratio is always more favourable for a company.
- The higher turnover ratio shows that the company is using its assets more efficiently.
- The lower turnover ratio shows that the company is not using its assets efficiently.
It is calculated by comparing net sales with average total assets.
Asset turnover = Net Sales Revenue/Average Total Assets
ASSET VERIFICATION
Asset verification is a process of making accurate information on assets. It is the process which shows the proper valuation of assets.
The verification process includes verifying:
- The existence of the assets.
- Correct valuation
- Condition of the assets.
- Location of the assets.
- Legal ownership of the assets.
Objectives of verification are:
- To show the correct valuation of the assets.
- To ensure that the assets have been recorded in a proper manner.
- To find out whether the assets were in existence or not.
- To detect errors and fraud, if any.
- To know the condition of the assets.
ASSET FREEZE
Frozen assets mean that assets which are owned but cannot be sold, used. It usually happens in the case of debt which needs to be paid and the assets remain frozen until such debt have been paid. In other words, you can say, the blocking of financial assets of a person.
ASSET TRACKING
It is a method used to track the physical assets, either by scanning the barcode labels or by using tags using GPS, BLE which broadcast their location.
Benefits of Asset Tracking
- Easily locate assets at any time.
- Track and reduce asset loss.
- Helps in utilising assets more effectively.
- You can immediately know where your assets have been allocated.
- To know the maintenance schedule and status of the assets.
- To know about your organization’s physical assets.
ASSETS: DEBIT OR CREDIT
Assets in ledger are recorded as debit when they are increased while they are recorded as credit when they are decreased. In simple words you can say that debits are increases in asset account where as credits are decreases in asset accounts. Debit is an entry made on the left side of an account
- Debit is an entry madeon the left side of an account.
- Credit is an entry made on the right side of an account.
- Asset increases – Debited.
- Asset decreases – Credited.
HOW ASSETS AFFECT THE BUSINESS?
Recording the Assets accurately in the balance sheet can help you in many business-related events such as tax bill, etc. Assets can help you to:-
- generate income
- raise your income value
- to increase the running efficiency of your business.
Assets are categorized on the basis of their liquidity, which means the ease of transferring the Assets into Cash.
- Fixed Assets cannot generate the cash flow easily as they take a long procedure to convert into the cash.Example:- Land, Building, etc.The value of Fixed Asset is decreased with time. This decrease in the value of the Assets is known as the Depreciation. Depreciation or decrease in the value of the Fixed Asset is recorded as the company’s expenses. Recording the depreciation expense in the balance sheet will decreases the tax value of the Asset.
- Current Assets are also called Liquid Assets or Short-term Assets as they can be easily convertible into cash.Example:- Fixed deposit, Bank balance, etc.They increases the cash flow.
- Tangible Assets are those assets which we can feel, touch and see. In other words, you can say those Assets which have a physical existence. So, all Fixed Assets are categorized as Tangible Assets because of there physical existence.They have the same affects on the business as the Fixed Assets have, but they are easily convertible into cash in the case of those Current Assets which has physical existence such as, Cash.
- Prepaid expenses hurt cash flow when business paid money in advance for the services which have not incurred.
- Accounts receivable affects the cash flow of the business. This shows that much money the business have to receive from the customers who bought products on credit. This asset is a promise of cash that business will receive.
In simple words you can say that Assets help you to facilitate the running efficiency of your business.
ASSET VS LIABILITY
Assets are meant for:-
- Which puts money in your pocket.
- Helps in generating future income.
- It is something you have control over.
- Things has a monetary value.
- Which can be easily converted into cash.
HOW ASSETS TURN INTO LIABILITIES?
Sometimes Asset turns into Liability when it becomes responsible for increasing your expenses. It only depends on the fact that how you are using it.
Let’s have an example of a house:-
- A house is not useful in generating income but sometimes, it becomes useful in generating income. Otherwise, it comes with many expenses such as taxes, maintenance, etc.
- A house/home is an asset if you are renting it but it becomes a liability if you are living in it. Some people thought that it is an Asset. But it is an asset because it is your property. You can get some of your money back for you had been spent on its purchase or more than for its purchase, it only depends on the market value. So, whatever you get high market price or low, the only thing you will get by selling your house is the cash and hence, cash is an asset.
- But it is a liability when you are living in it because you have to pay for taxes, maintenance cost, insurance, etc. In this way, the money will go out of your pocket. Because when you are living in your house then, it means it is not making money or you can’t earn money from it. Here, the house is a liability because in that case, a house takes more money out of your pocket every month than it puts in it.
- If you are renting your house instead of living in it than, it will put monthly income in your pocket. Here, the house becomes an asset because now, it helps generate cash flow.
- A house is either an asset or a liability. If it makes you money then, it is an asset and if it costs you then, it is a liability.
Liabilities are meant for:-
- Money goes out of your pocket or income.
- Responsible for causing expenses.
- Loss of money as a result of a past event.
- Results in the outflow of economic resources.
HOW LIABILITIES CAN TURN INTO ASSETS?
Liabilities can turn into your assets if they start adding money in your pocket. Sometimes an increase in an asset can be as a result of an increase in liability.
Let’s have an example of a car:-
- Rohit wants to have their car. But he does not have much money to buy it. He decided to take a loan to buy it. But after buying the car he felt that it is much expensive deal than he was expected. Because the car comes with its expenses such as; taxes, insurance, maintenance cost, fuel, repair cost, etc. So, in this case, the car becomes a liability for Rohit.
He adopted an idea that he will use this car only when he actually felt the need for a car. He means that he will use the car when he goes out with their family. He decided to rent the car when not using it. Then, it will make money for him. And hence, this liability will turn into an asset for Rohit, when it will earn for him.
In this way, you can turn your liabilities into assets. Instead of making cheques every month for the maintenance, interest on the loan, you can change your liability into an asset by having few ideas and implement on them.